Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring: Fact vs. Fiction (Addressing the FDA Warning)
Hey there, health tech enthusiasts and anyone curious about the latest gadgets! We’ve all seen the sci-fi movies where a quick scan of your hand tells you everything you need to know about your health. And with the rise of smart rings, it feels like we’re getting closer, right? From tracking sleep to monitoring heart rate, these little bands of tech are pretty amazing. But there’s one particular promise that’s been buzzing around, and it’s a big one: smart ring blood glucose monitoring.
Sounds incredible, especially for the millions of people living with diabetes. Imagine, no more finger pricks! Just glance at your ring, and boom, you know your blood sugar. If you’ve been following the news, you might have even seen some hype around it.
But here’s the thing, and it’s a pretty important “thing”: Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring isn’t quite there yet. And to underscore this, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently issued a pretty stern warning about smartwatches and smart rings claiming to measure blood glucose levels.
Let’s dive into what’s fact, what’s fiction, and why this FDA warning is so crucial.
My Personal Dive into the Smart Ring Hype
I’ve always been a bit of an early adopter when it comes to tech. My first smartwatch felt like a gadget from the future, and when I heard whispers about Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring, my ears perked up. I even found myself scouring Kickstarter and obscure tech blogs, hoping to find that magic device.
I remember thinking, “This could be a game-changer!” I have family members with type 2 diabetes, and I’ve seen firsthand the daily routine of finger pricking and careful tracking. The idea of a non-invasive, Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring continuous glucose monitor (CGM) in a sleek ring form factor seemed like a dream come true.
But as I dug deeper, the more I realized that while the desire for this technology is huge, the actual science behind it for consumer-grade devices just isn’t there yet. And that’s exactly what the FDA is trying to tell us.
The FDA Warning: What You Need to Know
In February 2024, the FDA released a public safety communication specifically warning consumers against using smartwatches or smart rings that claim to measure blood glucose levels.
Why the warning?
The FDA stated very clearly that these devices have not been authorized, cleared, or approved for this purpose. That means their accuracy and reliability for Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring measurement are completely unproven.
Think about it: Your blood glucose levels are critical for managing diabetes. Incorrect readings can lead to serious health consequences, like administering the wrong dose of insulin or not seeking medical attention when blood sugar is dangerously high or low.
Here’s the crux of it: The Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring unauthorized devices could give you wildly inaccurate readings, leading to poor health decisions. And that’s a risk no one should take.
How Do Current Blood Glucose Monitors Work?
To understand why a Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring solution is so challenging, let’s briefly look at how current, FDA-approved methods work:
- Finger-Prick Glucose Meters: These involve pricking your finger to get a small drop of blood, which is then applied to a test strip. The meter analyzes the blood directly for glucose content. This is a very direct and accurate method.

- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These devices use a tiny sensor inserted just under the skin (usually on the arm or abdomen) to measure glucose in the interstitial fluid (the fluid between your cells). This fluid mirrors blood glucose levels, and CGMs provide readings throughout the day and night, offering a comprehensive picture of glucose trends.

Why is Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring So Hard?
This is the million-dollar question! Glucose is present in various body fluids, but accurately measuring it externally, without drawing blood or inserting a sensor, is incredibly complex.
Here are some of the scientific hurdles:
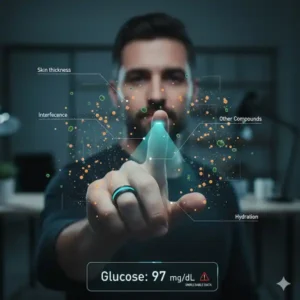
- Specificity: How do you isolate the glucose signal from all the other things happening in your body? Your skin, sweat, and other bodily fluids contain countless compounds.
- Accuracy and Precision: Even if you can detect glucose, can you do it with the level of accuracy needed for medical decisions? A few milligrams per deciliter off could have serious implications.
- Interference: Things like skin temperature, hydration levels, skin thickness, and even motion can interfere with optical or electrical signals trying to detect glucose.
- Calibration: Approved devices often require calibration (e.g., with a finger prick) to ensure accuracy. How would a non-invasive device maintain consistent calibration?
Many smart rings use optical sensors (like photoplethysmography or PPG) to measure heart rate or blood oxygen. These work by shining light into the skin and detecting how much is reflected. While ingenious for those purposes, directly measuring glucose from these signals is a huge leap.

So, What About the Future? Is There Any Hope?
Absolutely, there’s hope! The scientific community is intensely focused on developing truly non-invasive Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring. Researchers are exploring various promising technologies, including:
- Advanced Optical Methods: Using different wavelengths of light or spectroscopy to detect glucose signatures more accurately.
- Microneedle Patches: Tiny, painless needles that barely penetrate the skin to sample interstitial fluid, offering a less invasive alternative to current CGMs.
- Radiofrequency (RF) Technology: Using radio waves to detect glucose levels.
Many major tech companies and medical device manufacturers are pouring resources into this area. When a truly accurate and reliable non-invasive glucose monitoring device emerges, you can bet it will undergo rigorous testing and receive FDA approval. Don’t give up, Smart Ring Blood Glucose Monitoring may work some day with the needed approvals.
My take? We’re probably still several years away from consumer-grade smart rings or watches offering accurate, medically reliable blood glucose monitoring. When it does arrive, it will be a huge deal, and it will come with proper validation and regulatory approval.
What Should You Do if You See a Device Claiming to Measure Blood Glucose?
- Be Skeptical: If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- Check for FDA Approval: For any medical device, especially one that impacts critical health decisions, always look for clear indications of FDA authorization, clearance, or approval. If it’s not there, avoid it.
- Consult Your Doctor: If you have diabetes or are concerned about your blood glucose, talk to your healthcare provider. They can recommend appropriate, proven methods for monitoring and management.
- Prioritize Proven Methods: Stick with FDA-approved blood glucose meters and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) that your doctor prescribes or recommends.
Additional Helpful Content: Living with Diabetes
While we wait for the future of non-invasive tech, let’s remember the foundations of managing diabetes:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on whole foods, limit processed sugars and refined carbohydrates.
- Regular Physical Activity: Even moderate exercise can significantly improve blood glucose control.
- Medication Adherence: Take your medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Regular Monitoring: Use your approved glucose meter or CGM consistently as advised by your healthcare team.
- Stress Management: Stress can impact blood sugar levels. Find healthy ways to cope.
- Regular Doctor Visits: Keep up with your appointments to ensure your treatment plan is effective and to address any concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Are there any smart rings that do measure blood glucose accurately? A: As of now, no smart ring has been authorized, cleared, or approved by the FDA (or similar regulatory bodies worldwide) to accurately and reliably measure blood glucose levels for medical decision-making.
Q: Can my smartwatch or smart ring help with diabetes management in other ways? A: Yes! Many smartwatches and rings can track activity levels, sleep patterns, and heart rate. These metrics can indirectly support overall health and well-being, which is beneficial for diabetes management. However, they are not a substitute for direct blood glucose monitoring.
Q: How can I tell if a device is FDA approved? A: Reputable medical devices will clearly state their FDA clearance or approval on their packaging, in their user manuals, or on the manufacturer’s website. You can also search the FDA’s databases for approved medical devices.
Q: What are the risks of using an unapproved blood glucose monitoring device? A: The main risk is inaccurate readings, which can lead to dangerous health decisions. For example, if a device falsely shows normal blood sugar when it’s actually very high, you might delay crucial treatment. Conversely, a false low reading could lead to unnecessary emergency treatment.
Q: When can we expect accurate smart rings for glucose monitoring? A: While many researchers are working on it, there’s no definitive timeline. The science is complex, and regulatory approval takes time. It’s safe to say it’s still several years away for consumer-ready, medically accurate devices.
Additional Helpful Links
- Read about using your smart ring for home control – Smart Ring Smart Home Control: The Magic on Your Finger
External Links for Authoritative Sources:
- FDA Safety Communication: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/do-not-use-smartwatches-or-smart-rings-measure-blood-glucose-levels-fda-safety-communication
- American Diabetes Association: https://www.diabetes.org/
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes
Stay informed, stay safe, and always prioritize your health with proven, medically-approved methods!